Financial services institutions, such as banks and insurance companies, rely on transparency of their customer master data and product master data to capitalise on a number of industry trends
Master data management plays a critical role in ensuring data transparency. Master data management therefore enables you to leverage the customer and product master data – that you already have – to address and drive revenue from these current trends in the financial services industry.

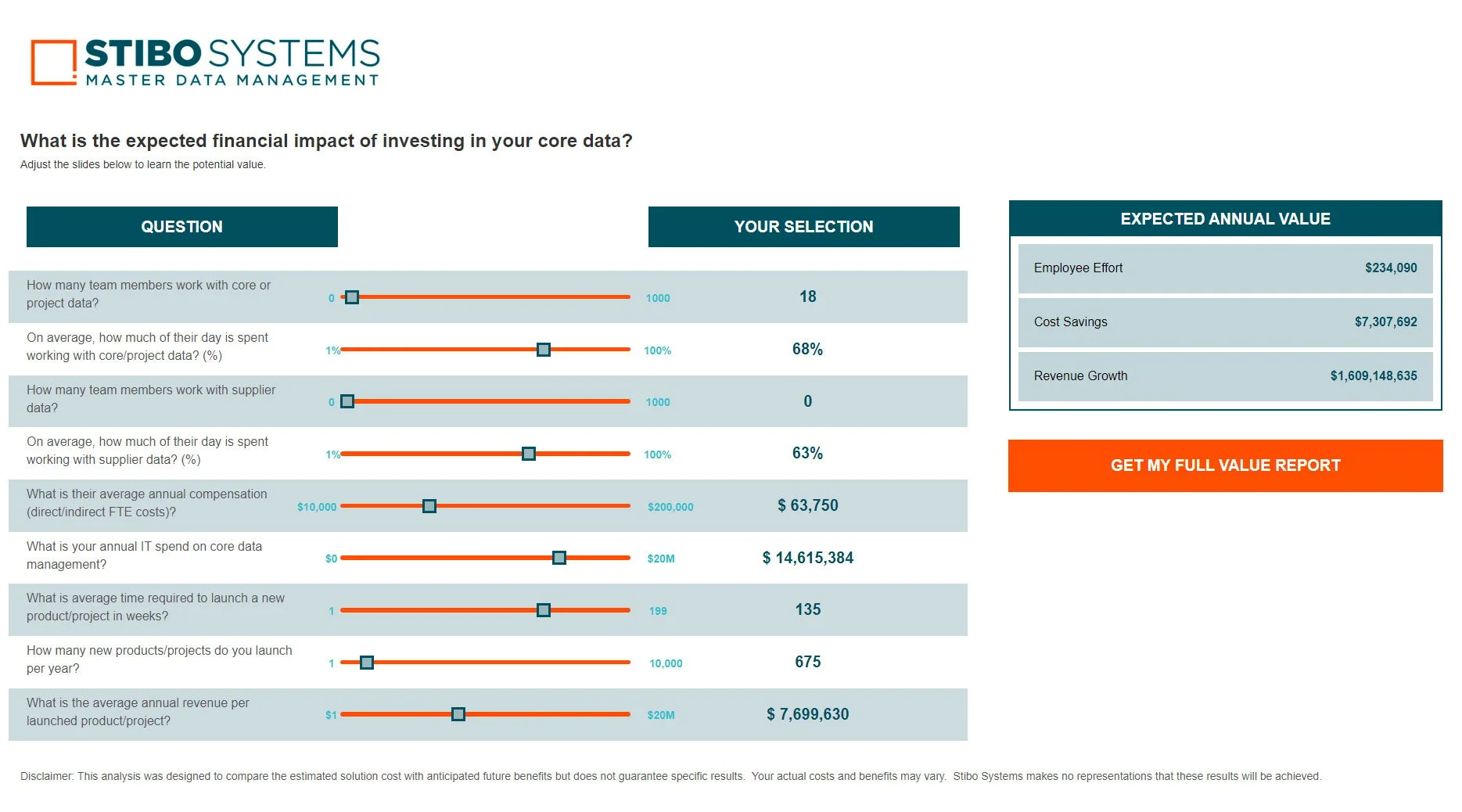
Get the full executive brief on the top ten trends in financial services and exactly how master data management can help you to address and capitalise on those trends, or get a quick summary below.
10 trends in financial services that make master data management essential
Trend #1: Partnering with digital service providers, fintechs and industry disruptors
Banks are morphing into becoming technology companies. To support this paradigm, financial services providers need to implement scalable mechanisms by which they can collaborate on the development of new products and services with new types of business partners.
Trend #2: Putting AI and ML into accelerated training with synthetic data
As AI moves from the testing phase to finding full employment, it needs to be trained with synthetic data that reflects real-world use cases and allows it to explore the corners of exceptions. Robotic process automation (RPA) will benefit from this training as it moves towards becoming more intelligent (IRPA).
Trend #3: Establishing a data culture with data democracy
Being a highly data-intensive business, financial services companies rely on the ability to confidently make decisions based on data. Implementing reliable, data-driven decision-making processes requires that you develop awareness of the impact of data management. This is often referred to as a data culture.
Trend #4: Becoming customer and solution-centric
Offering a seamless customer experience is still a key component of any customer loyalty initiative. To treat a customer as unique, you need to make product portfolios work together to form part of a personalised solution, rather than an abstract set of products.
Insurance Customer Want Solutions, Not Products
Get the White Paper
How master data management underpins innovation in the business model
Trend #5: Cultivating the digital twin
As customer expectations continue to evolve, the ability of financial services providers to meet them will largely depend on access to ever more insightful and personal information. You need to develop operational and analytical systems in order to help turn your data points into a digital twin of the customer that provides more actionable insight.
Trend #6: Offering customer service at the point of need
Using personal interaction channels in conjunction with automated services is not just reserved for direct banking applications, but now extends to the point of need.
Trend #7: Selling your data
Good data has commercial value. The discipline of infonomics provides support to the mechanism of linking information to monetary value. Financial services companies have the opportunity to find new revenue streams from data assets, such as customer data.
Trend #8: Implementing proactive compliance management with regtech
Compliance measures are data intensive. Regulatory technology, regtech, is a technology that supports the implementation of regulatory processes. The use of regtech is increasing.
Trend #9: Making transparency part of the brand
Privacy, consent and transparency of products and operations are increasingly of concern to consumers. Addressing transparency can help you to build consumer trust and thus turn regulatory compliance into a business advantage. Learn more about how to make your financial products and processes
transparent to the delight of consumers and regulators in the white paper below.
Financial Services: Creating New Value for Your Customers With PIM
Get the white paper
Learn how to make your financial products and processes transparent
Trend #10: Building a business-as-a-service
Like many businesses, financial services organizations are evolving into a provider of digital services via platforms, effectively putting the business “in a box”. If you want to pursue this ambition, your data not only needs to be of high quality. It also needs to be served up according to contextual business information views, rather than technical views.
The critical role of master data management in financial services
The common denominator of the top trends in financial services is that they rely on data transparency. Master data management enables data transparency by providing a single, trusted view of business-critical information, such as customer and product master data.
Master data management defines and implements governance policies to certify that certain critical parameters of your customer and product data, including its origin, accuracy, coherence, accessibility, security, auditability and ethics, are under business supervision and best serving business purpose.
Adding a little bit more detail, this means that master data management can help by:
- Providing the ability to create, manage and distribute the authoritative sources of reference data required for open banking collaboration
- Providing the data governance that can help to support the explainability of the AI decision making (XAI) to ensure non-bias
- Establishing and monitoring data governance policies, yielding metrics that support improvement planning
- Allowing data governance to stretch across and join product and customer data sets (Multidomain MDM)
- Providing a unified offer development platform that helps to describe offers and the parameters to which they might be personalized according to customer insight
- Creating trusted customer data sources that maintain insightful data collected from the customer and other inferred sources
- Linking the quality, coherence and depth of information to rules of individual consent
- Providing the ability to manage the safeguards of transparency on the key business facts that often form part of compliance reporting
- Constructing a single, 360° view, of the customer